Sea snakes are interesting creatures that live in marine environments for most of their lives. These snakes are excellent swimmers, and dive to hunt underwater – and can stay submerged for long periods.
In general, sea snakes can not breathe underwater. However, they can hold their breath for long periods of time. Sea snakes can hold their breath and stay underwater anywhere from 30 minutes to over 8 hours, depending on the species, and level of activity.
For example, an inactive sea snake may be able to stay underwater for several hours. An individual that is hunting, on the other hand, may need to surface more frequently.
That said, recent scientific discoveries suggest that some sea snakes may have a limited ability to breathe underwater by absorbing oxygen through the skin (Read on for more information on that).
Sea Snakes Have Lungs and Breathe Air
Like all reptiles, snakes have lungs, that they use to breathe air.
Due to their elongated bodies, snakes do not have lungs that are located side to side, like ours.
Instead, they have one shorter and one very long lung in a series. In most species, the left lung is the smaller one, and is roughly 85% of the length of the elongated right lung.
Some species only have one elongated lung, and the smaller lung is absent.
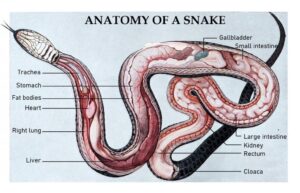
The longer lung occupies around 30 percent of the body length in boas (Boidae), and as much as 80 percent of the body length in some colubrids (Colubridae) and elapids (Elapidae). Sea snakes generally fall into the Elapidae family.
In many snakes, the smaller left lung is vestigial, and all gas exchange happens with the longer lung.
How Snakes Breathe
To breathe, snakes take air down into their lung (s). Once the air is in the lungs, oxygen from the air is then absorbed into the snake’s bloodstream. At the same time, carbon dioxide from the bloodstream is diffused into the air.
That said, it’s important to note that snakes do not possess a diaphragm, to move air in and out of their lungs, as mammals do.
Instead, they respire using their ribs.

In between each rib, are muscles that help force air out of the lungs.
To breathe in, the muscles contract, and air rushes into their lungs -and to breathe out, the muscles relax and, air leaves the lungs.
While underwater, sea snakes return to the surface periodically to replenish their oxygen stores and expel waste gases – with their lungs.
Sea snakes have nostrils with valves consisting of specialized spongy tissue to exclude water. In addition, their windpipe can be drawn up to where the short nasal passage opens into the roof of the mouth.
This adaptation allows them to have their heads partially submerged when they surface to breathe air.
Sea Snakes Can Stay Underwater for a Long Time
Although sea snakes are air-breathing reptiles, they can stay underwater for long periods of time.
Depending on the species, sea snakes can stay under anywhere from 30 minutes, to several hours – possibly as much as eight or more.
For example, Olive sea snakes (Aipysurus laevis), are known to be able to spend up to two hours underwater before returning to the surface to breathe.

Apart from species, the level of activity also affects how long a particular sea snake can stay submerged.
A resting sea snake may be able to stay submerged for several hours, while an individual who is actively hunting may need to resurface more frequently.
Some Sea Snakes May Be Able to Breathe Underwater
Although sea snakes need to resurface to breathe air, some species have found ways to top up their oxygen levels while submerged.
A team of researchers analyzed the bodies of two blue-banded sea snakes (Hydrophis cyanocinctus) – and discovered a gill-like network of blood vessels in the animals’ heads.

This complex system of blood vessels is known as a modified cephalic vascular network (MCVN).
It is located just under a broad area of skin between the snout and the roof of the snake’s head.
While the MCVN is structurally very different from the gills of fish, its function is similar. It provides a large surface area packed with oxygen-depleted blood vessels.
The oxygen-poor blood in these vessels is able to absorb oxygen from the surrounding water – through the skin.
The blood oxygenated blood is then carried to the brain – very similar to how a fish’s gills work.
In this way blue-banded sea snakes use the top of their head, as a sort of gill, to breathe underwater.
This ‘skin breathing’ is known as cutaneous respiration, and is very unusual for reptiles, because their skin is thick and scaly.
That said, sea snakes with the ability to breathe underwater still need to surface in order to breathe air, but the MCVN allows them to do so much less frequently than would otherwise be the case.
Can Sea Snakes Drown?
Despite their various adaptations to marine life, sea snakes can drown if they can not surface for air.
For example, if a sea snake is entangled in a ghost net, oxygen stores will deplete rapidly and the snake may drown if it is unable to reach the surface.
Common Questions
How Long Can Sea Snakes Stay Underwater?
How long a sea snake can stay underwater depends on the species. For example, Olive sea snakes are able to stay underwater for up to two hours. Some sea snake species may be able to sit underwater for as long as 8 hours.
In addition, activity level affects how long a particular sea snake can stay underwater.
Think about it, when we are running or jogging, we breathe heavier and in much quicker breaths than when we are at rest.
For sea snakes, this is also true. They will have a higher oxygen demand when they are very active in the water (escaping a predator or chasing prey, for example), and a lower oxygen demand when they are inactive.
For this reason, an inactive sea snake will be able to stay underwater for much longer than an active individual.
How Long Can Sea Snake Hold Their Breath?
Depending on the species and activity levels, sea snakes can hold their breath anywhere from 30 minutes to over 8 hours.
However, some sea snakes have evolved the ability to exchange some oxygen and carbon dioxide with the water through their skin. So they aren’t really holding their breath when submerged.
Featured image credit: Franco Colnago (CC BY-NC 4.0 DEED).
Sources:
By Douglas Mader, M.S., DVM, DABVP. Snake Anatomy: Know your snake inside and out with this snake anatomy introduction. (PDF).
Palci, A., Seymour, R. S., Nguyen, C. V., Hutchinson, M. N., Lee, M. S. Y., & Sanders, K. L. (2019). Novel vascular plexus in the head of a sea snake (elapidae, hydrophiinae) revealed by high-resolution computed tomography and histology. Royal Society Open Science, 6(9), 191099. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.191099
Wikipedia. Sea snake. Accessed at: https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Sea_snake
Hi, my name is Ezra Mushala, i have been interested animals all my life. I am the main author and editor here at snakeinformer.com.

